Understand the 499 status code Client Closed Request error: What are the causes and how to fix it.
What is the 499 Client Closed Request error?
The 499 HTTP is a non-standard status code introduced by Nginx when a client, for instance a browser, closes the connection while Nginx is processing the request.
How to fix the 499 Client Closed Request error
There are various reasons why the client would not process the request and ended up with a 499 error code. In the following sections, we will help you identify the different causes and how to fix them in each case.
499 error when the website is behind a proxy
You may find 499 errors when you have a Load Balancing service between your users and your Nginx. A similar situation occurs when your Nginx site is served by a CDN or is behind a WAF (Web Application Firewall).
The 499 error happens when the front server attending your browser request is an Nginx server in reverse proxy mode, and it sends the request to your server site, but your site process exceeds the waiting time of the front server.
To fix this error, you can:
- Increase the processing capacity of your application server. By increasing the “processing power”, you will reduce the waiting time of the Nginx clients in front of your service.
- If you cannot increase the power of your application server, then increase the timeouts of your proxies (load balancer, CDN, firewall, …).
At Wetopi you can increase the size of your server with a single click.
★ Zero-config: configuration files for all server services are transparently adjusted to the power.
The right way to set the timeouts
If there are proxies on your setup such as a “Load balancer”, a Firewall, a CDN, etc, you should set the timeouts so that you timeout first your application server and then the other proxies to the user.
Example:
User → CDN → Nginx Load Balancer → Nginx application → Php_fpm
It’s recommended to set the timeouts like this:
- n seconds to
Php_fpmtimeout.
Set thephp.inimax_execution_timeand
therequest_terminate_timeoutin yourphp_fpmconfig file.
- n+1 seconds to Nginx application timeout.
Set thefastcgi_read_timeoutin your nginx config.
- n+2 seconds to timeout to Nginx Load Balancer
In your location doing theproxy_passset the timeouts of:proxy_connect_timeoutproxy_send_timeoutproxy_read_timeout - n+3 seconds of timeout for your CDN. NOTE: If you can’t set the timeouts of your CDN, then find what is its timeout and adjust the others according to it.
It provides a correct chain of timeouts: Setting an incremental chain of timeouts lets you find who is reaching the timeout.
499 when your server closed the connection
This could be your case, If:
- your site is running with an Nginx server and,
- the request is passed to an application processor e.g.
php_fpm, or - the request is passed to your API
This setup is configured using the nginx fastcgi_pass directive.
This 499 error code is produced when your server is too slow.
e.g. your WordPress page process takes too long or freezes
To correct this error, you can:
- Increase the processing capacity of your server. By increasing “processing power”, you will reduce the period Nginx waits.
- If you cannot increase your server power, increase Nginx timeouts with the directive:
fastcgi_read_timeout.
How to fix the 499 error when your application dies
If your application dies without an answer, the solution could be in your API or CGI code.
NOTE: This is the least common case, PHP and other processors always throw a note to notify a problem. If the app was throwing an error, Nginx would pass you a 5XX error code, not a 499.
If your application freezes, you have 2 options:
- First, tell the Nginx to wait longer. Increase the timeouts of your Nginx by modifying the
fastcgi_read_timeout. - If waiting longer does not solve the problem, increase the processing capacity of your server.
- If the 499 error occurs on a specific page or request, it could be a “hung” or “code freeze” in your application or content manager. If you use WordPress, check plugin compatibility. If database queries are made, check the good status of tables and indexes.
499 when your server is under a DOS or DDOS attack
There might be a case when someone attacks, and intentionally consumes the server resources. This makes the server unable to process the request and return the result on time.
To verify if this is your case: look at your analytics, and search for spikes in traffic with requests giving the 499 status code:
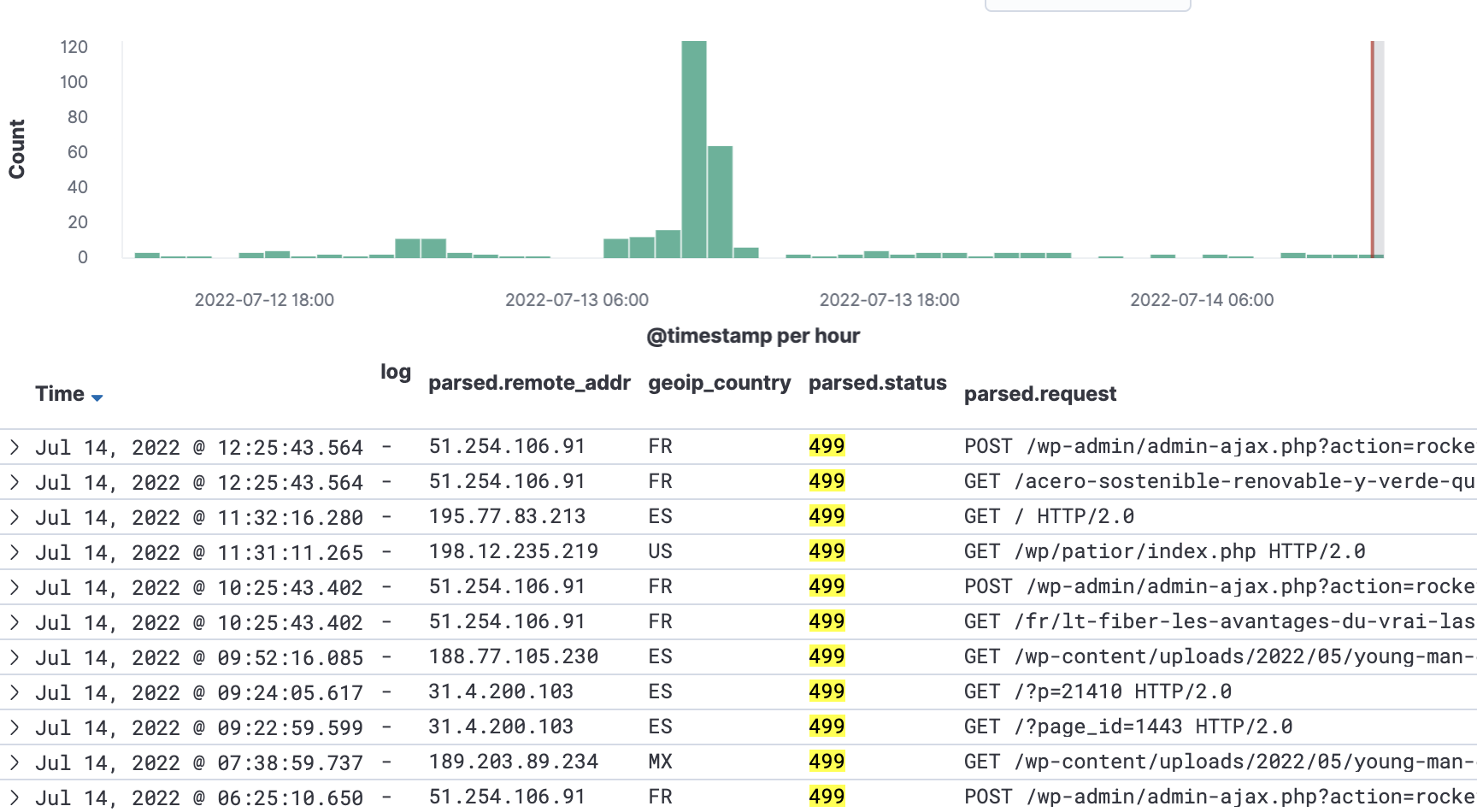
How to fix the 499 error when DOS/DDOS attacks:
In this case, the best solution is a combination of security measures:
- Prevention: avoid non-legit traffic. You can filter malicious traffic with a combination of public and private blacklists.
- Add infrastructure protection against DOS (Denial of Service) and DDOS (Distributed Denial of Service). Find a hosting provider with infrastructure ready to mitigate this kind of attack.
- Add a protection layer, a security proxy, in front of your server, or
- Add an external security service. A well-known one is Cloudflare. They put a distributed infrastructure in front of your server to fight against DDOS attacks.
As WordPress specialists, we know how important it is to add strong measures of security.
Shared security heuristic learning,
We apply three techniques to filter traffic:
Blacklisting from external sources and
Mitigation of DDoS attacks.
Don’t you have an account on Wetopi?
Free full performance servers for your development and test.
No credit card required.
All HTTP Status Codes
200 OK
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-Authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
402 Payment Required
404 Not Found
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I’m A Teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
501 Not Implemented
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
506 Variant Also Negotiates
507 Insufficient Storage
508 Loop Detected
510 Not Extended
511 Network Authentication Required
599 Network Connect Timeout Error