The 400 Bad Request HTTP error code is a common issue that users can encounter when browsing the web. In this article, we will explore the causes of this error and provide you with some tips on how to troubleshoot and fix it. By the end of this post, you should have a better understanding of what causes the 400 Bad Request error and how to fix it.
What Is The 400 Bad Request Error?
This error occurs on your browser or “client side” when something is wrong with your request that the server cannot process.
As mentioned in the RFC 9110 HTTP Semantics by the IETF HTTP Working Group, the 400 (Bad Request) status code indicates that the server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing).
Different 400 Error Messages
Depending on the web server, or browser, you may find different descriptive messages for this error:
- 400 Bad Request.
- Bad Request.
- This page isn’t working. If the problem continues, contact the site owner. HTTP ERROR 400
- This page isn’t working at the moment. If the problem persists, contact the site owner. HTTP ERROR 400
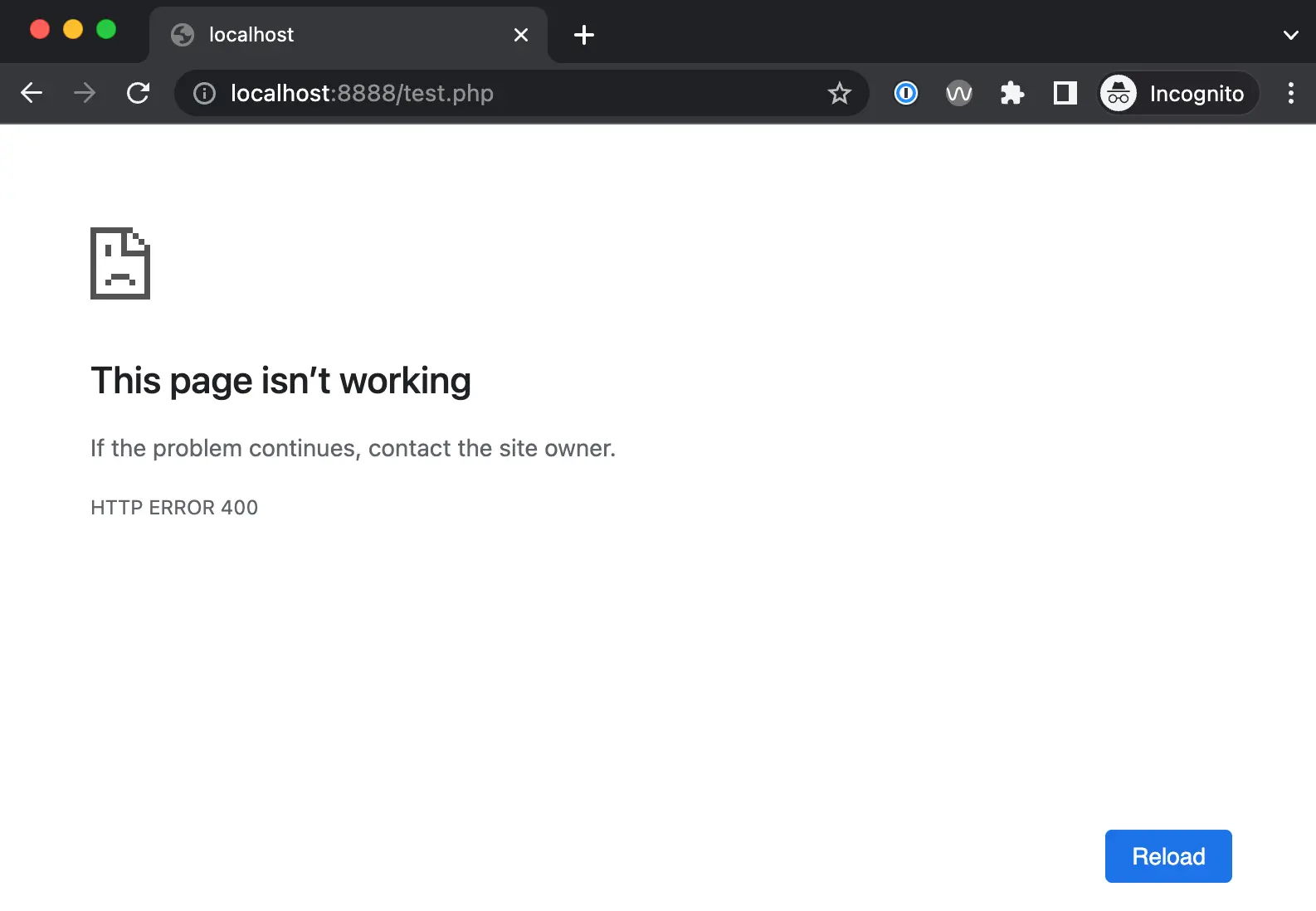
The default 400 Bad Request Error displayed in OSX Safari looks like a blank page:
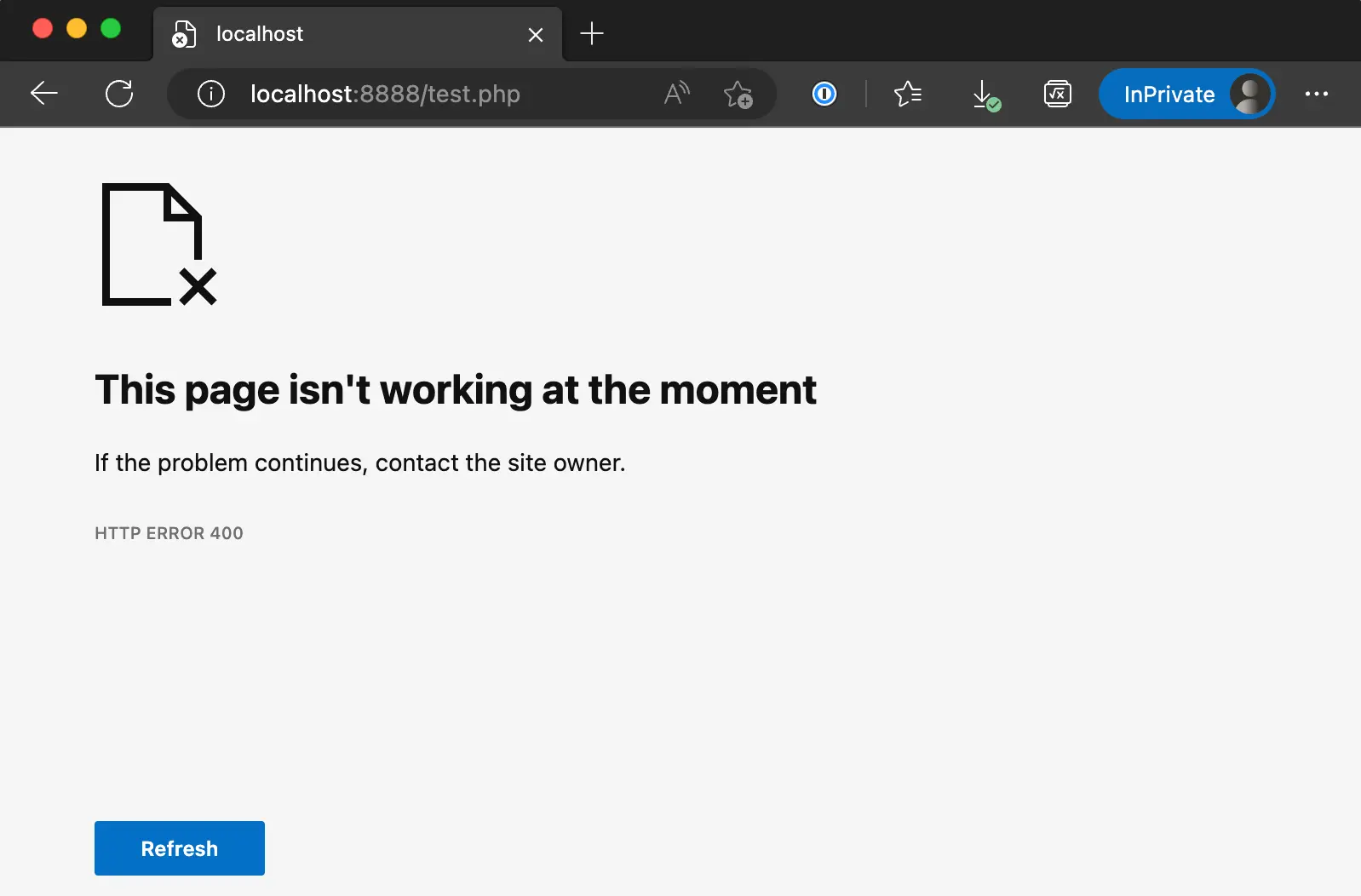
On Microsoft Edge, the Error will show this:
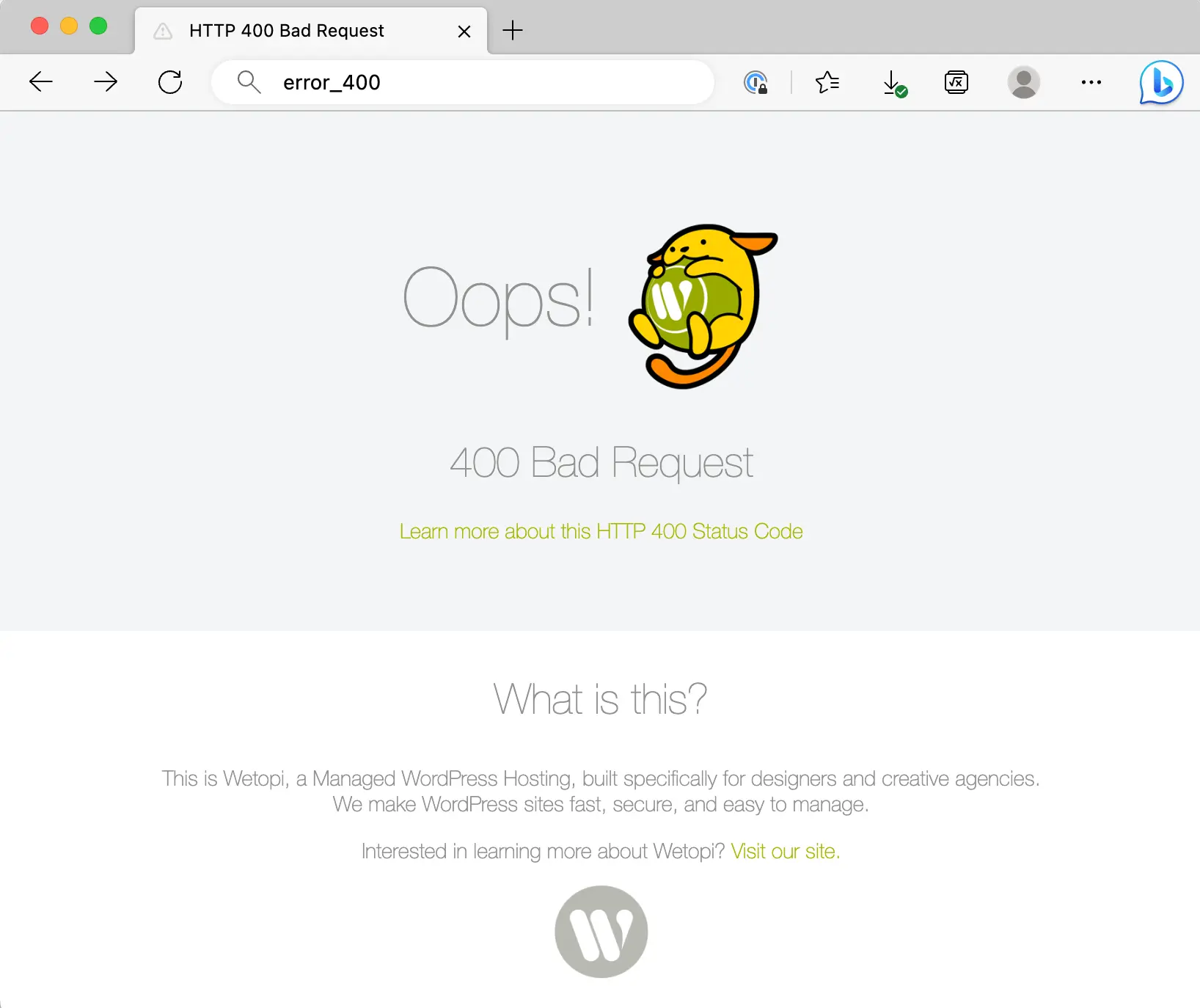
Some hosting servers can provide their own error page, like our Wetopi Load Balancer 400 Error:
We help you throughout the process
It doesn’t matter if you have one WordPress site or 100, our team is ready to carefully migrate your websites for free.
When migrating a website, we manually monitor it and verify its security.
400 Bad Request Causes
As per its definition earlier, a 400 Bad Request Error occurs when the web server can’t process something on your end. But don’t let a 400 Bad Request Error ruin your browsing experience! Check out the most common reasons behind this error:
1. 400 Error In The URL String Syntax
A 400 Bad Request error can occur if the URL is typed incorrectly, contains malformed syntax, or includes illegal characters. It may happen by mistake if we manually type the address, in particular if the URL has encoded chars (the ones that start with the %)
2. 400 Error In the Request Headers
For example, one of the HTTP headers is malformed, or its size exceeds the maximum limit allowed by the server.
An HTTP header contains information about the request, such as the browser type, the URL, and the type of data sent. If the header is incorrect or too large, the server won’t be able to process the request and will return a 400 error code.
3. 400 Error In the Cookies
Cookies are a way for websites to store data on a user computer to remember their preferences, login information, and other details. However, like HTTP headers, cookies can also cause a “400 bad request” error if they are formatted incorrectly or exceed the server size limits. Some examples are:
- If a website sets a cookie with a name that contains spaces or special characters, it may cause a “400 bad request” error if the cookie is not properly encoded or formatted. For example, a cookie with the name “my cookie” should be encoded as “my%20cookie” to be valid.
- Another example of a malformed cookie is when it contains invalid characters or values. For instance, if a cookie value contains a semicolon or a comma, it can confuse the server cookie parsing algorithm and cause a “400 bad request” error.
- Finally, cookies can exceed the server size limits, causing a “400 bad request” error.
4. 400 Error In the request Body content
When submitting content to a website, users may encounter a “400 Bad Request” error if the data sent to the server has an error or exceeds a limit. For example, if a user tries to upload a file to a website, and it exceeds the server file size limit, the server will reject the request and return the “400 Bad Request” error.
Similarly, if the user enters invalid or incomplete data in a form, the server may also reject the request and return the error message.
Need guidance?
Wetopi
In front of a demanding project?
Read this post about the top five criteria to select a hosting when you are a business
How To Fix The 400 Bad Request Error Code
Be sure to follow the next steps to fix the 400 error:
1. Verify the URL
The most common cause of a 400 Bad Request error is a mistake in the URL entered in the browser address bar. It could be due to typos, missing or incorrect characters, or an outdated or invalid URL. Double-check the URL, spelling, and formatting, especially if the address has encoded chars.
If the error persists, the next step is to clear the session storage and cookies in relation to the domain you are browsing. Keep reading:
2. Clear the Session Storage
When we remove all the Session Storage information for the page showing the error, we remove cookies, cache, and locally stored information.
How to clear the Session Storage on a Chromium-based (Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, or any other browser that uses the Chromium engine):
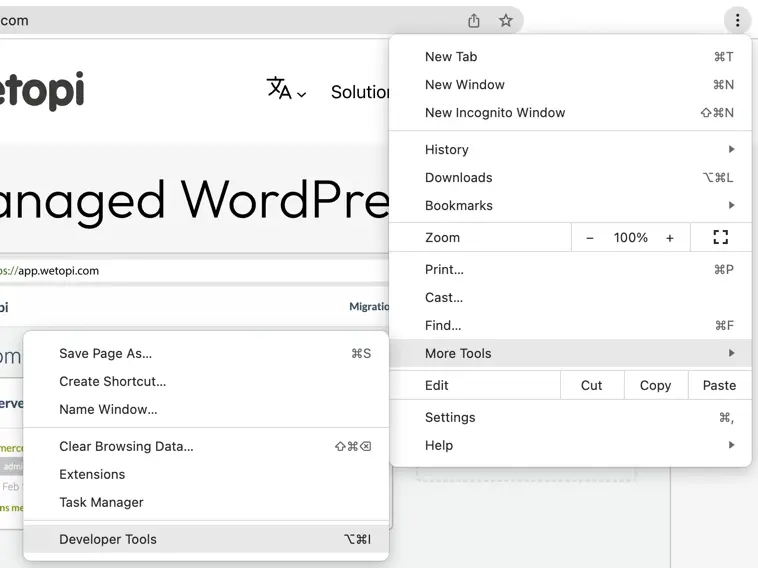
- Open the browser and click the three dots icon in the top-right corner.
- Click “More tools” and then “Developer tools” or use the keyboard shortcut “Ctrl+Shift+I” (Windows) or “Cmd+Option+I” (Mac).
- Select the “Application” tab and then click “Storage” in the left-hand panel:
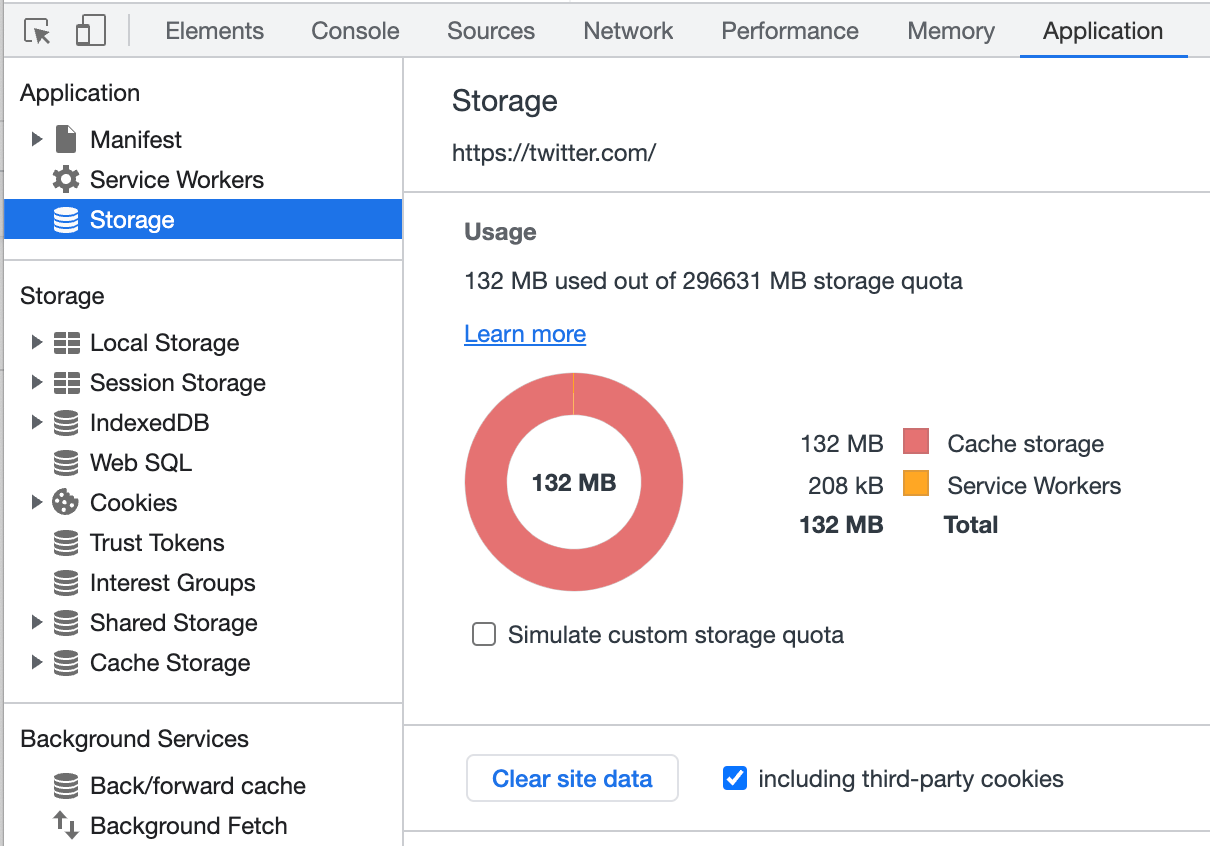
- In the right-hand panel click the “Clear site data” button.
At that stage, just reload the page and see if things are working again.
3. When Uploading a file, check the size
If you’re experiencing the 400 Bad Request Error while uploading a file, as a test, try using a much smaller file to see if the error goes away.
If this previous test works, then you know that the 400 Error is related to the Upload File Size limits of the server.
4. Inspect the logs
If the previous fixes do not solve the problem and you encounter the “400 Bad Request” error on your website, it could indicate a general problem with the server.
You can inspect the server logs for more information. Server logs should be accessible for clients in any hosting company, although sometimes they may be hard to locate or access.
If your WordPress site is hosted on a Wetopi server, you can easily access the logs with just two clicks.
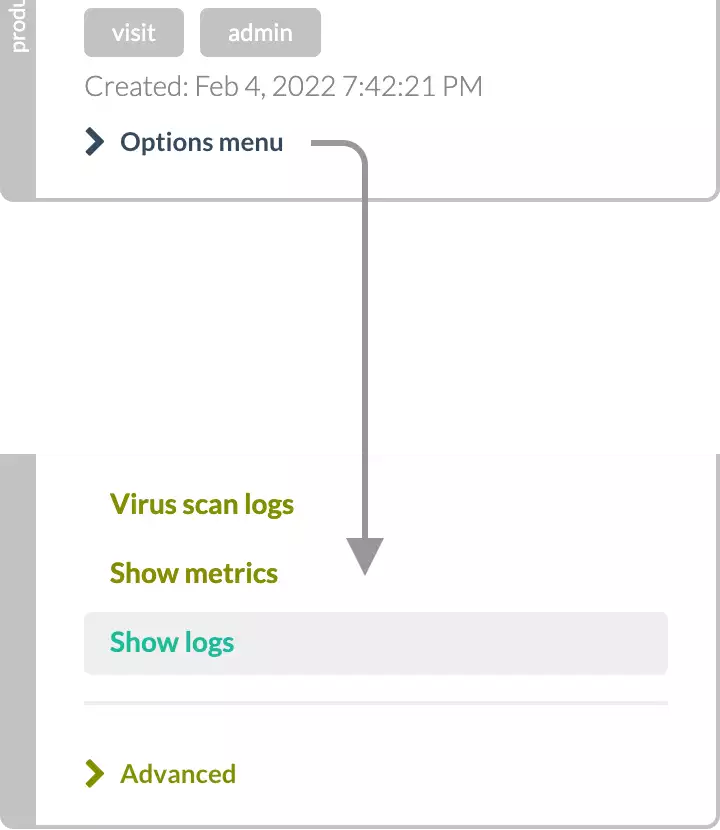
- Open the Options Menu
- Click Show logs:
Summary
The 400 Bad Request HTTP error code occurs when there is something wrong with the request made by the client side that the server cannot process.
This could be due to various causes:
- an error in the URL string syntax
- an error in the header request, cookies, or body content request.
In this article, we have suggested ways to fix this error by:
- verifying the URL entered,
- clearing the session storage,
- or inspecting the logs.
Don’t you have an account on Wetopi?
Free full performance servers for your development and test.
No credit card required.
All HTTP Status Codes
200 OK
201 Created
202 Accepted
203 Non-Authoritative Information
204 No Content
205 Reset Content
206 Partial Content
207 Multi-Status
208 Already Reported
226 IM Used
300 Multiple Choices
301 Moved Permanently
302 Found
303 See Other
304 Not Modified
305 Use Proxy
307 Temporary Redirect
308 Permanent Redirect
402 Payment Required
404 Not Found
406 Not Acceptable
407 Proxy Authentication Required
408 Request Timeout
409 Conflict
411 Length Required
412 Precondition Failed
413 Payload Too Large
414 Request-URI Too Long
415 Unsupported Media Type
416 Requested Range Not Satisfiable
417 Expectation Failed
418 I’m A Teapot
421 Misdirected Request
422 Unprocessable Entity
423 Locked
424 Failed Dependency
426 Upgrade Required
428 Precondition Required
429 Too Many Requests
431 Request Header Fields Too Large
444 Connection Closed Without Response
451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons
501 Not Implemented
505 HTTP Version Not Supported
506 Variant Also Negotiates
507 Insufficient Storage
508 Loop Detected
510 Not Extended
511 Network Authentication Required
599 Network Connect Timeout Error